Material properties are defined on the Material Properties Spreadsheet and then are referred to as you build beams, columns, and walls.
You may perform analysis using any type of material; simply define the
properties for the material here. You may use up to 500 materials
in a single model although most models will only have one or two.
The Material Properties Spreadsheet records the material properties to be used in the model
and may be accessed by selecting Materials

 button on the Window Toolbar.
button on the Window Toolbar.
Label is the material label you wish
to use to describe the entered material properties. This label is
how you will reference the set of properties later when defining
E is Young's modulus that describes the material stiffness.
G is the shear modulus and may be left blank if you would like it calculated automatically. The equation for “G” is:
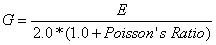
Note
Nu is Poisson's
ratio.
Therm is the coefficient of thermal
expansion and is entered per 10^5
(100,000) degrees.
Density is the material density
and is used in the calculation of the member
Yield is the yield stress and is used only for Hot Rolled and Cold Formed steel design.
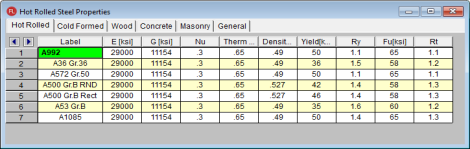
The Hot Rolled tab records a number of hot rolled steel specific material properties that do not exist for the other materials. These entries are described below:
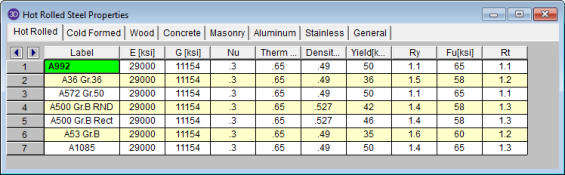
Ry is the ratio of the expected yield stress to the specified minimum yield stress. This value is used in determining the required strength of an element for the seismic detailing checks.
Rt is currently not used by the program. In a future version of the program this value will be used to calculate the expected tensile strength for the seismic detailing checks.
The Cold Formed tab records a cold formed material property that may not exist for the other materials. This entry is described below:
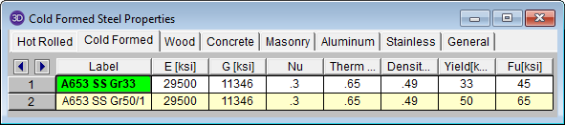
Fu (Ultimate) is the ultimate tensile stress.
The Wood tab records a number of wood specific material properties that do not exist for the other materials. These entries are described below:
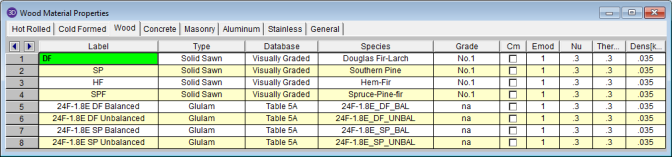
Type - Currently there are four wood types available: Solid Sawn, Glulam, SCL (this includes LVLs), and Custom.
Database - Based on your Type selection, the Database menu will filter to the appropriate databases.
Species - Based on your Database selection, the Species menu will filter to the appropriate databases. This is the wood species designation from your selected design code.
Grade is the wood grade designation from your selected design code. This has a drop down list where you can select the appropriate grade.
The Cm check-box determines if the wet service / moisture content factor should be applied. If you put a check in the Cm field, the appropriate factors will be applied to the allowable stresses and Young’s Modulus (E).
The Ci check-box determines if the incision factor should be applied. If you put a check in the Ci field, the appropriate factors will be applied to the allowable stresses and Young’s Modulus (E).
Emod is a factor that is applied to the Young’s modulus modifier to reflect the NDS Appendix F criteria. This is not applicable to the CSA O86 design code.
Note:
Commercial Species Groups:
When either the NDS 05/08, 12, 15, 18, or 24 wood design code is selected, the Solid Sawn Species menu lists two new species listed that are not specifically shown in the NDS code. These are the Commercial Species Group I - DF/SP and Commercial Species Group II - HF/SPFe Fir. These are meant to be simplified groupings of the most commonly used wood species. It is meant to simplify the selection procession for wood member design in the United States.
The design values for Group I take the NDS allowable stress values for two of the most widely used species (Doug Fir-Larch and Southern Pine) and uses the lower bound allowable stress value for each size and grade.
Similarly, the design values for Group II take the allowable stress values for Hem Fir and Spruce-Pine-Fir and use the lower bound allowable stress values for each size and grade.
The Concrete tab records a few concrete specific material properties that do not exist for the other materials. These entries are described below:
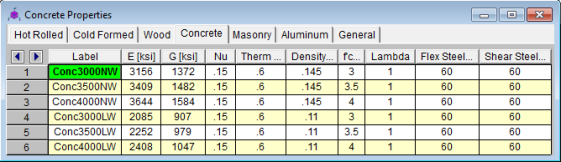
f'c is the concrete compressive strength used for concrete design.
Lambda, λ is the lightweight concrete modification factor. This factor only applies to the ACI 318-14, ACI 318-11, ACI 318-08 and CSA A23.3-04 codes. For all other codes the Density value of the material determines any strength reduction.
Flex Steel is the reinforcement yield strength for flexural bars in members and vertical bars in walls. Shear Steel is the reinforcement yield strength for shear bars in members and horizontal bars in walls.
The Masonry tab records masonry specific material properties. Here we will describe items that do not exist for other materials.
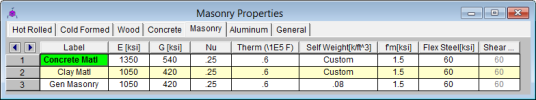
Masonry Self Weight can be accounted for by two different methods. Entering a number for the density will result in masonry walls which have a self weight equal to that density multiplied by the wall cross-sectional area. Otherwise, click within the cell to launch the masonry self weight dialog:
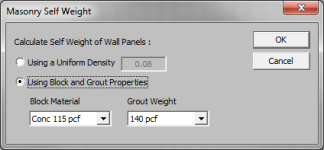
Set the Using Block and Grout Properties option to have the program automatically calculate the self weight of the wall using the weights from tableB3 of the Reinforced Masonry Engineering Handbook (RMEH). The self weight will be listed as Custom.
f'm is the masonry compressive strength used for masonry design.
Flex and Shear Steel are the rebar yield strengths for flexural and shear bars used to reinforce the masonry.
Note:
- Masonry Shear Steel is automatically set to the Flex steel strength.
- Masonry materials are used only for walls in wall footings. See the Wall Footing Definitions spreadsheet for more information.